The 21st century has refined digital literacy. It has broadened its perspective to include other aspects of the 21st context. These literacies include ¹Cyber Literacy or Digital Literacy, ²Media Literacy, ³Arts and Creativity Literacy, ⁴Financial Literacy and lastly Multi Cultural Literacy or Global Literacy.
In the past few decades, technology has spanned the globe, connected people in a whole new way. As a result, citizens of all countries have not only had to learn to use new technology, but also learn how to interact with one another. Skills that compromise these abilities have been combined under the term "digital literacy".
What are Digital Literacy?
Digital Literacies are the individual's capabilities to be able to effectively and responsibly function and perform in a digital society. Almost two decades ago, Paul Gilster (1997) defined digital literacy as the "ability to understand and use information in a multiple formats from widerange of sources when it is presented via computers" . Gilster coined the term "digital literacy" and it came on the discussion of the concepts on (a) visual literacy when images and non-verbal symbols try to capture the knowledge; (b) technological literacy requiring one to be able to use technology in addressing a need; (c) computer literacy, which in the 1980s started to become a household item manipulated to achieve one's target; and (d) information literacy which refers to the trending, evaluating, using and sharing of information.
The Digital Literacies
- Media Literacy is one's ability to critically read information or content and utilize multimedia in creatively producing communications.
- Information Literacy is locating information from the web and interpreting while evaluating its validity in order that it cab be shared.
- ICT Literacy is knowing how to select and use digital devices, applications or services to accomplish tasks requiring the use of internet.
- Communication and Collaboration are one's capabilities in being able to participate in the digital networks in the teaching and learning context.
- Identity Literacy is being able to understand how to ensure safety and security in managing online identity and foster a positive digital reputation.
- Learning Skills are ways of knowing how to study and learn in technology enriched environment.
- Digital Scholarship is being able to link and participate in professional and research practices.
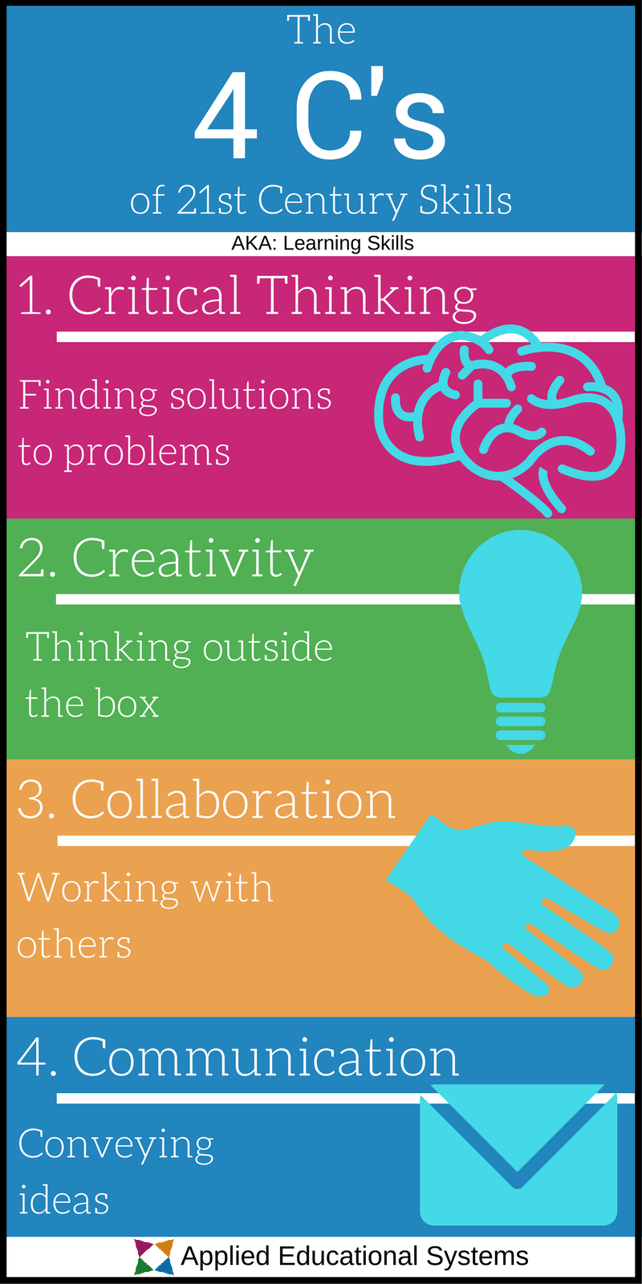
The four C's of the 21st Century Skills refer to critical thinking, creativity, communication, and collaboration. To perform you need to develop and enhance these skills.
- Critical Thinking is a learning of how to solve a problems. It is the ability to differentiate facts from opinions and not only just learn a set of facts or figures but also discover these for the sake of knowing what ought to be.
- Creativity is the process of thinking outside of the box. While creativity is often treated like a you-have-it-or-you-don’t quality, students can learn how to be creative by solving problems, creating systems, or just trying something they haven’t tried before. That doesn’t mean every student will become an artist or a writer. Instead, it means they’ll be able to look at a problem from multiple perspectives — including those that others may not see.
- Collaboration is the practice of working together to achieve a common goal. Virtually every job requires someone to work with another person at some point, even if it’s for something as simple as what to get for lunch. Practicing collaboration helps students understand how to address a problem, pitch solutions, and decide the best course of action.
- Communication is the practice of conveying ideas quickly and clearly.
Not yet.
In the age of text-based communications — SMS, emails, social media, etc. — it’s never been more important for students to learn how to convey their thoughts in a way that others can understand them.
That’s because text-based communications lack tone, which is critical to understanding the context of someone’s words.
In addition to the 4 C's, there areCitizenship and Character.
Citizenship is known as netizenship in the virtual world. This is making the person consider how one behaves accordingly by observing the norms and rules that are in accordance with what are sociably and virtually acceptable.
As a result, one is projecting reputable digital identity which is his or her character.
Digital Literacy Skills vs. Digital Literacy: What's the difference?
As teachers, why do we need to worry about digital literacy if our students are already growing up surrounded by technology?
While there’s no doubt that being adept at using digital tools and technologies is essential for everyone in the 21st century - teachers and students alike - possessing digital skills is not the same as being digitally literate. It’s a mistake to assume that exposure to digital tools and technologies automatically equates to the knowledge of how to use these effectively.
Our students are tech-savvy digital natives. They know their way around a tablet, smartphone and laptop better than most. More often than not, they know how to do a voice search on an iPad, share selfies on Instagram, play a video game and send a GIF on WhatsApp.
But what they lack is the knowledge of how to use these digital tools and technologies to communicate and achieve their learning goals.
Lynch (2017), identified eight digital literacy needed to become digitally literate. These are:
1. Coding
Coding is a universal language.
Basic understanding of HTML, CSS and the like will create a shared understanding of what can be done with the web page.
Basic understanding of HTML, CSS and the like will create a shared understanding of what can be done with the web page.
2. Collaboration
Collaboration is the use of Google Docs among others allows student to begin experimenting with effective online collaboration.
3. Cloud Software
Cloud Software is essential part of document management. It is used to store everything from photos to research projects, to term papers and even music.
4. Word Processing Unit
Word Processing Unit Google, Microsoft Online Drop.Box are available for storage and management solution.
5. Screencasting
A screen cast is a video recording using computer screen and usually includes an audio.
6. Personal Archiving
Personal Archiving the students should be taught the concepts of metadata, tagging, keywords, and categories to make them aware how are they represented online.
7. Information Evaluation
Information Evaluation critical thinking to weed out fake news is a crucial 21st century skill. The use of tools and skills needed to process information are very much needed.
8. Use of Social Media
Social media serves different purposes depending on the user, technology and need.
Here are examples of how Digital Skills or Proficiency support Digital Literacy.
Our students not only need to be proficient in how to use digital technologies - they also need you to work proactively to embed digital literacies into your curriculum. Without this, they cannot be truly digitally literate, defined by the American Library Association as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.”
It’s important for students to critically think about media and the messages they get daily. The ability to weed out fake news, for example, will be a crucial 21st-century skill. We need to give our students the tools and skills needed to process the vast amounts of information they’re exposed to each day.
A recent Digital Literacy Impact Study showed that learners with a solid grounding in digital literacy have a competitive advantage in the workforce. Because digital literacy is so essential not only to our students’ academic and future career success but also their ability to fully participate in modern society, teaching digital literacy is quickly becoming a critical part of the curriculum at the K-8 level.
In short: if digital literacies haven’t yet become a core component of your classroom learning experience, it's time to rethink your teaching strategy.
References:
Medlock Paul, Casey & Spires, Hiller & Kerkhoff, Shea. (2017). Digital Literacy for the 21st Century. 10.4018/978-1-5225-7659-4.ch002.
https://www.teachaway.com/blog/digital-skills-vs-digital-literacy-whats-difference?amp
https://www.aeseducation.com/career-readiness/what-are-the-4-cs-of-21st-century-skills
https://youtu.be/A6k82xAK5ns
Here are examples of how Digital Skills or Proficiency support Digital Literacy.
Digital Skills
|
Digital Literacy
|
Sending an email, DM or text.
|
The ability to judge the appropriate digital channel for online communication with peers, teachers and parents.
|
Using Microsoft Office/Google G Suite.
|
The ability to:
|
Tweeting, posting to Facebook, uploading a video to YouTube, adding to a Snapchat story and posting a photo to Instagram.
|
The ability to navigate social media safely, in order to:
|
Conducting a Google search.
|
The ability to effectively use online search as a research tool, including:
|
Our students not only need to be proficient in how to use digital technologies - they also need you to work proactively to embed digital literacies into your curriculum. Without this, they cannot be truly digitally literate, defined by the American Library Association as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.”
It’s important for students to critically think about media and the messages they get daily. The ability to weed out fake news, for example, will be a crucial 21st-century skill. We need to give our students the tools and skills needed to process the vast amounts of information they’re exposed to each day.
A recent Digital Literacy Impact Study showed that learners with a solid grounding in digital literacy have a competitive advantage in the workforce. Because digital literacy is so essential not only to our students’ academic and future career success but also their ability to fully participate in modern society, teaching digital literacy is quickly becoming a critical part of the curriculum at the K-8 level.
In short: if digital literacies haven’t yet become a core component of your classroom learning experience, it's time to rethink your teaching strategy.
References:
Medlock Paul, Casey & Spires, Hiller & Kerkhoff, Shea. (2017). Digital Literacy for the 21st Century. 10.4018/978-1-5225-7659-4.ch002.
https://www.teachaway.com/blog/digital-skills-vs-digital-literacy-whats-difference?amp
https://www.aeseducation.com/career-readiness/what-are-the-4-cs-of-21st-century-skills
https://youtu.be/A6k82xAK5ns




Hi Ma'am Ashielah! Your blogspot is one of the best! You're like an expert blogger. I couldn't even tell that it is your first time!
ReplyDeleteThank You po ma'am! :)
Delete